Treatment of melanoma
Diagnosis of melanoma
The suspicious skin spot will first be cut away and sent to the laboratory for examination. If this examination shows that it is a melanoma, a second operation will follow in which more skin will be removed. A sentinel node excision or lymph node dissection is sometimes performed to check for metastases to the nearest lymph nodes.
Once the melanoma has been confirmed, the laboratory will also check whether the melanoma has a certain genetic mutation. Almost 50% of melanomas have a BRAF mutation. BRAF mutations generally have high-risk disease characteristics, poorer survival rates, and possibly more aggressive disease
Some other investigations that can also be done are:
- CT/PET/MRI scan
- Ultrasound
- Blood tests
Treatments for melanoma
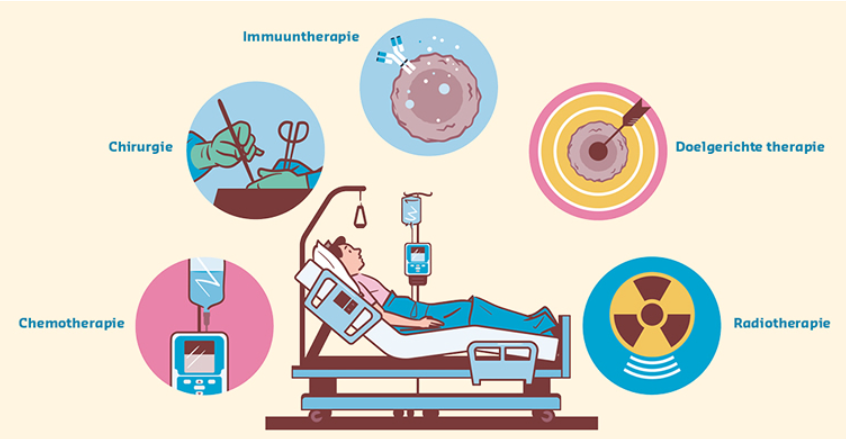
Much progress has been made in the treatment of melanoma in recent years. Depending on the stage of melanoma, different treatment options are now available:
Currently, only high-risk melanomas from stage II will be treated.
Whether or not to treat and with which therapy of course depends on the personal situation of the patient.
What treatments are available for melanoma?

Targeted therapies are only used in melanoma that has a genetic mutation in the BRAF gene. These therapies block the BRAF and MEK proteins, thus preventing the uncontrolled cell growth and/or the spread of cancer cells. Targeted therapies can be used in the adjuvant setting (stage 3 or 4 after tumour removal) or in the metastatic setting (stage 4 where the tumour cannot be removed and has spread)
Current targeted therapies are taken daily and are pills/capsules.

Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy acts on the immune system to enable it to recognise and attack cancer cells as invaders. The use of immunotherapy causes a response in which the patient’s immune cells attack the melanoma cells and prevent their spread, which can lead to the regression of the tumours.
Immunotherapy can be used in the adjuvant setting (stage 2 with high risk, or stage 3 or 4 after tumour removal) or in the metastatic setting (stage 4 where the tumour cannot be removed and has spread)

Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is proposed as treatment for advanced or metastatic melanoma. It is given when no other treatment is possible.

Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is usually prescribed after surgery to treat any remaining cancer cells or when surgery is not possible. It can also be used to treat pain or other symptoms.


